Rainwater harvesting is the practice of collecting and storing rainwater for future use. It involves the collection of rainwater from rooftops, surfaces, or other catchment areas and directing it to a storage system, typically a tank or cistern. This stored water can then be used for various purposes, such as irrigation, watering plants, domestic use, and replenishing groundwater.
Rainwater harvesting offers several benefits, including:
- Water conservation: By collecting rainwater, you reduce the demand for freshwater from other sources, such as rivers, lakes, or underground aquifers. This helps conserve water resources and reduces the strain on existing water supplies.
- Self-sufficiency: Harvested rainwater can provide a supplementary source of water, especially in regions where water scarcity is a concern or during drought periods. It can contribute to greater self-sufficiency and resilience in water supply.
- Cost savings: Utilizing rainwater can lead to cost savings on water bills, particularly for activities like irrigation or toilet flushing. Additionally, it can reduce the burden on stormwater drainage systems, potentially minimizing infrastructure costs.
- Groundwater recharge: In areas where groundwater levels are declining, rainwater harvesting can contribute to replenishing underground aquifers. By collecting rainwater and allowing it to percolate into the soil, it helps recharge groundwater and maintain ecological balance.
- Reducing runoff and flooding: Rainwater harvesting mitigates the effects of heavy rainfall by reducing surface runoff. This can help prevent soil erosion, minimize the risk of localized flooding, and improve water quality by reducing the pollution carried by runoff.
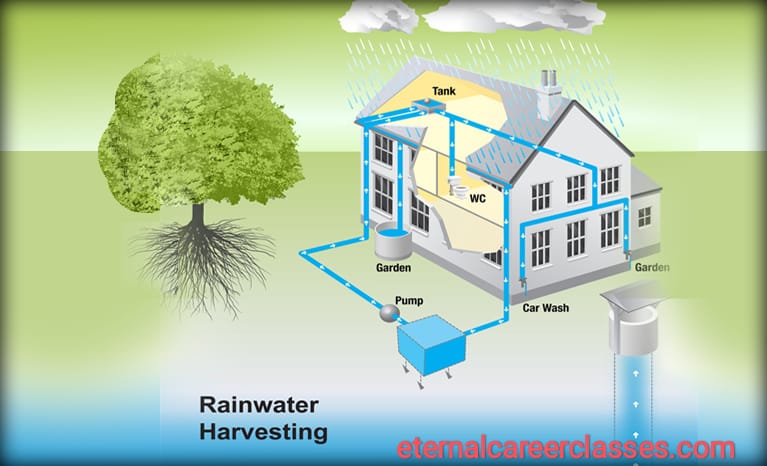
There are different types of rainwater harvesting systems, including:
- Rooftop rainwater harvesting: This method involves collecting rainwater from rooftops using gutters and downspouts. The water is directed into storage tanks or underground cisterns for later use.
- Surface runoff harvesting: This technique captures rainwater from paved or unpaved surfaces, such as driveways, roads, or open fields. The water is collected in channels or small ponds for storage or infiltration into the ground.
- Stormwater harvesting: This approach involves collecting rainwater from stormwater drains, retention ponds, or other urban infrastructure. The water is treated and stored for various purposes, such as irrigation or non-potable uses in buildings.
- Underground rainwater harvesting: In this system, rainwater is collected and stored in underground tanks or chambers. It is commonly used in areas where space is limited or aesthetic considerations are important.
It is important to note that the implementation of rainwater harvesting systems may require consideration of local regulations, the design of appropriate filtration and storage mechanisms, and regular maintenance to ensure the quality of stored water.
Overall, rainwater harvesting is a sustainable practice that promotes water conservation, self-sufficiency, and environmental resilience.

VISIT OUR OFFICE : 5TH FLOOR LE-DESIRE COMPLEX, CIRCULAR ROAD ,LALPUR, RANCHI, JHARKHAND
VISIT OUR WEBSITE FOR MORE INFOMATION HTTPS://ETERNALCAREERCLASSES.COM
FOR TEST SERISE, PREVIOUS YEAR QUESTION PAPER OF NEET AND DPP FROM ALL CHAPTERS ARE AVAILABLE ON ETERNAL RANCHI APP.DIRECT DOWNLOAD FROM QR CODE GIVEN BELOW
